Disclosure: As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases. This page may contain affiliate links, which means I may receive a commission if you click a link and purchase something that I have recommended. There is no additional cost to you whatsoever.
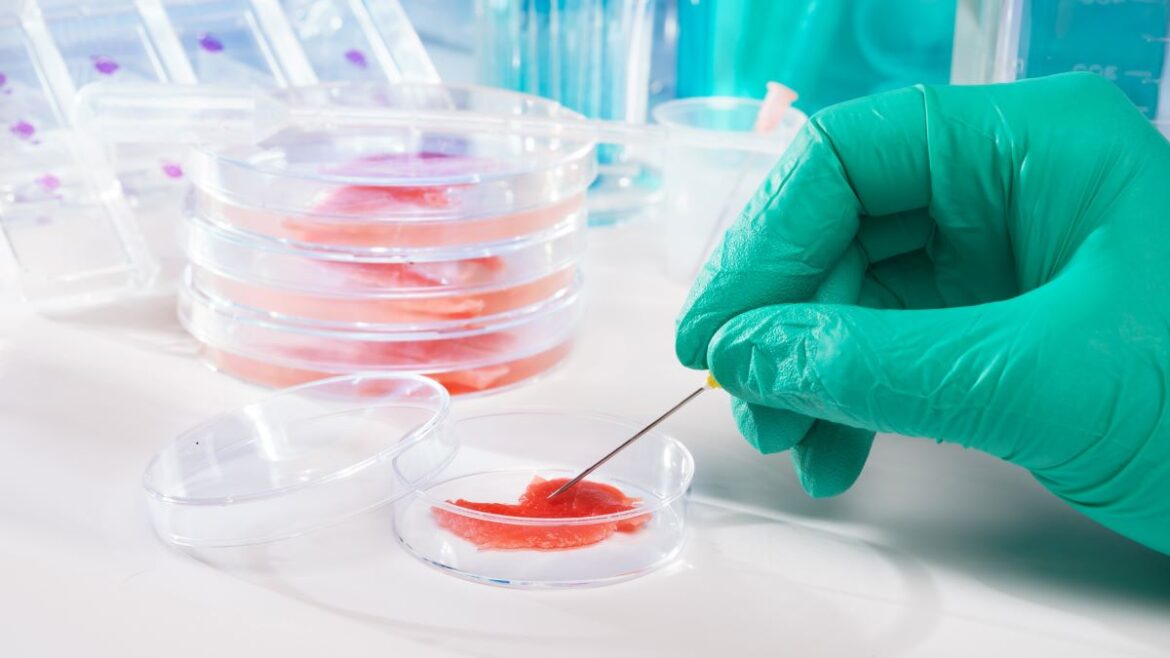
Lab-grown meat is a sort of cellular agriculture that grows proteins from a tradition, cell by cell, as an alternative of farming it. It’s additionally referred to as genetically-engineered or cultured meat in addition to test-tube meat and stem cell steak.
Singapore was the first country to approve a lab-grown meat product, bringing the potential for getting our dinner from scientists quite than farmers nearer than ever. But is it sustainable?
What’s the Logic Behind Lab-Grown Meat?
Cultured meat is broadly hailed for its potential to spare animal lives, reduce greenhouse gasoline emissions, and assist clear up the worldwide meals disaster.
Factory farming is an enormous problem. It’s energy-intensive, contributes to land, water, and air air pollution, and accounts for roughly 32% of global methane emissions. Methane is a strong greenhouse gasoline that contributes to local weather change. Plus, standard manufacturing facility farming practices are notoriously cruel to animals.
If the pandemic has taught us something, it’s that rampant food insecurity affects one in nine Americans, whereas worldwide, almost 2 billion people are meals insecure. The promise of lab-grown meat is an environmentally pleasant and humane protein supply for the world’s hungry. At least, in concept.
How Do Labs Grow Meat?
No animals are killed to develop meat in a lab. Instead, cells are taken from animal biopsies and grown by in vitro cell tradition. To develop animal tissue, labs use related methods to these utilized in regenerative drugs; the distinction is that they’re producing it from scratch. This entails intensive work to “feed” and preserve the classy meat.
Companies like Upside Foods (previously Memphis Meats), which has been engaged on cultured meat for years, dub the services the place they develop their meat merchandise “carneries” (a play on the phrase “breweries”). These services comprise large steel vats, referred to as bioreactors, with piping put in to flow into a “watery goo” that helps with tissue engineering. The “goo” consists broadly of amino acids, fat, nutritional vitamins, minerals, proteins, sugars, iron, insulin, oxygen — all the vitamins wanted to encourage cell development.
Is Lab-Grown Meat Safe for the Environment?
Because a lot continues to be based mostly on modeling, we don’t have arduous numbers for environmental affect but, however some early research estimate it might create more problems than it solves.
The Downsides of Lab-Grown Meat
Animal agriculture accounts for more than 14% of global GHG emissions attributable to human exercise, however lab-grown meat might, in truth, worsen climate change. Although it’s anticipated to provide extra CO2 than the stronger methane, CO2 takes for much longer to dissipate.
Plus, the inferred “cruelty-free” nature of lab-grown meat could be deceptive. The “goo” wanted to tradition the meat presently requires fetal bovine serum, which is obtained by a course of that raises ethical concerns.
Due to the numerous variables, manufacturing is very costly. When cultured meat turns into accessible for large consumption, it will likely be pricier than standard meat for a while — in 2013, this would have been $300,000 for one burger; at present, cultured meat would value nearer to $3,800/pound.
Some of those variables embrace vitality used (and emissions created) to tradition and nurture the meat; the necessity for sugar to feed the cells (seemingly from corn, which requires land use); and unclear plans for waste therapy at “carneries.”
The Upsides of Lab-Grown Meat
According to Dr. Carolyn Mattick, who conducts sustainability research on lab-grown meat, it seemingly wins in opposition to manufacturing facility farming with a drastically lower amount of water pollution and land use.
While there are issues over potential bacterial contamination of the cultures, there may be additionally the potential decreased danger of illness from meat produced with out livestock stored in such shut quarters. This might even assist convert farmers to the trigger in the long term.
Lab-grown meat can also change into a boon for meals safety. Although the method is dear now, Memphis Meats investor Ryan Bethencourt believes it has the potential to feed millions in the long run for $1-2/pound.
Ultimately, if scientists conclude cultured meat is healthier for the atmosphere, it might divert extra meat-eaters from the manufacturing facility farming established order. For many, the most important barrier to decreasing dietary meat consumption is cultural; some even imagine dominion over animals is a God-given right, which might make lab-grown meat a tough promote.
What’s within the Cards for Cultured Meat?
For the second, the thought of genetically engineering meat is slowed down in regulatory disagreements between the FDA and USDA. In the long run, widescale manufacturing of cultured meat would want cost- and resource-effective energy infrastructures to be possible.
It additionally wouldn’t substitute manufacturing facility farming anytime quickly. Steve Myrick, vp of operations at Upside Foods (previously Memphis Meats), says the present aim of cultured meat is to “augment, not disrupt” and “coexist, respect client traditions” with Big Meat.
As for the sustainability query, there are not any clear solutions but (however there’s a number of wholesome skepticism). Dr. Mattick says lab-grown meat is “not inherently better or worse, but different.” So, it’s not an automated win as some imagine — however it has potential.
Originally revealed on February 4, 2021, this text was up to date in January 2023.