Disclosure: As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases. This page may contain affiliate links, which means I may receive a commission if you click a link and purchase something that I have recommended. There is no additional cost to you whatsoever.
The Irish thinker George Berkely, finest identified for his concept of immaterialism, as soon as famously mused, “If a tree falls in a forest and nobody is round to listen to it, does it make a sound?”
What about AI-generated bushes? Probably wouldn’t make a sound, however essential nonetheless for issues like conservation efforts to adapt our city forests to local weather change. To that finish, scientists from MIT CSAIL, Google, and Purdue University’s novel “Tree-D Fusion” system merges AI and tree-growth fashions with Google’s Auto Arborist knowledge to create correct, 3D city bushes.

Sari Beeri, lead writer
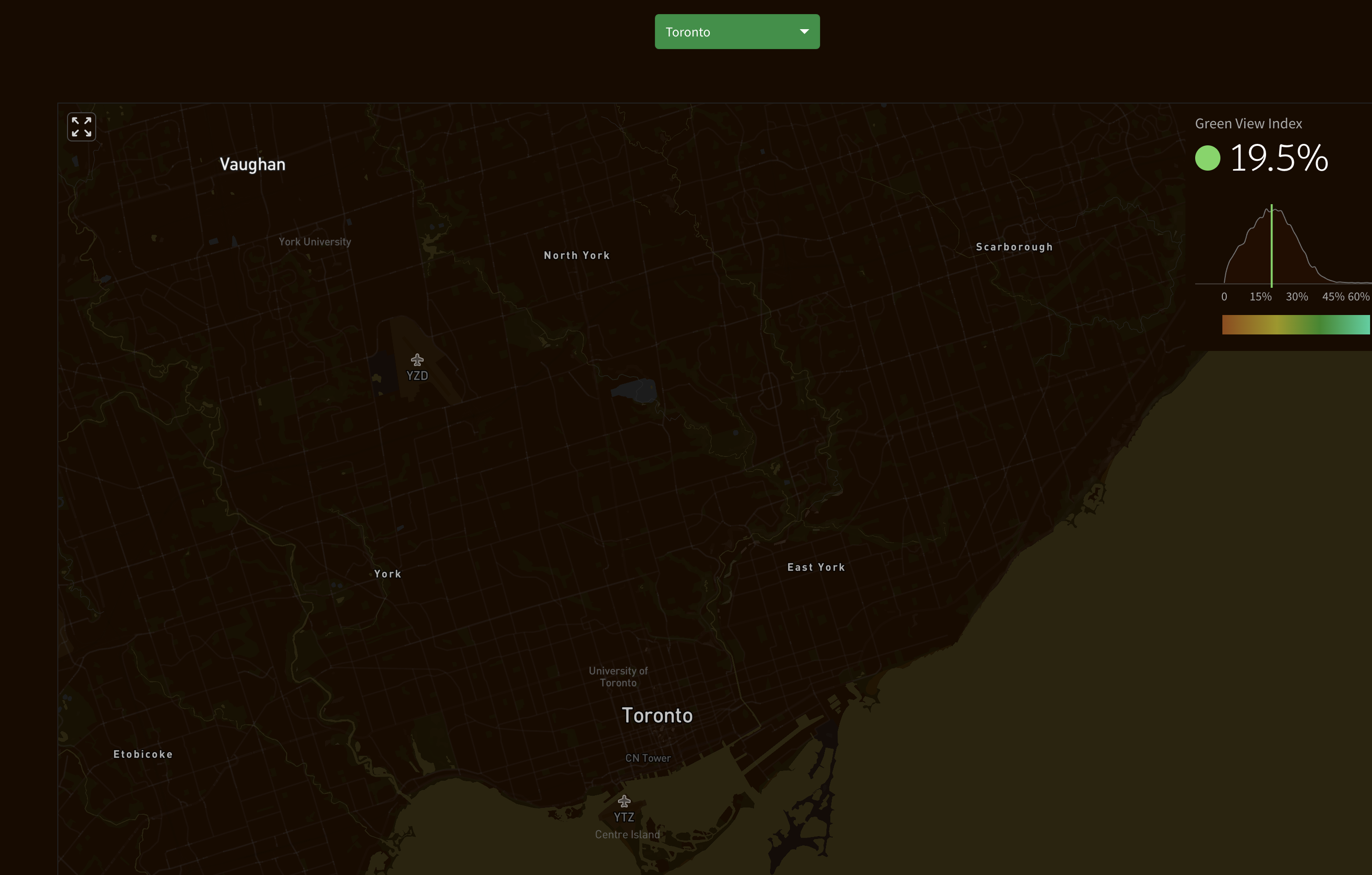
The venture produced the first-ever large-scale database of 600,000 environmentally conscious, simulation-ready tree fashions throughout North America. This helps city planners perceive the place they can build more green lungs. Cities like Toronto get a 17.5% inexperienced cover, whereas Tel Aviv will get a 17%.

“We’re bridging a long time of forestry science with trendy AI capabilities,” says Sara Beery, MIT EECS Assistant Professor and MIT CSAIL Principal Investigator, a co-author on a new paper about Tree-D Fusion. “This permits us to not simply establish bushes in cities, however to foretell how they’ll develop and influence their environment over time. We’re not ignoring the previous 30 years of labor in understanding find out how to construct these 3D artificial fashions, as an alternative, we’re utilizing AI to make this current data extra helpful throughout a broader set of particular person bushes in cities round North America, and finally the globe.”

Orange bushes assist passively warmth and funky on this Foster + Partners sustainable constructing. But are these sparsely planted bushes sufficient?
Tree-D Fusion builds on earlier city forest monitoring efforts that used Google Street View data, however branches it ahead by producing full 3D fashions from single photos. While earlier makes an attempt at tree modeling had been restricted to particular neighborhoods, or struggled with accuracy at scale, Tree-D Fusion can create detailed fashions that embody sometimes hidden options, such because the again facet of bushes that aren’t seen in street-view pictures.

A forest of bushes in Jaffa
AI bushes and implications for making cities cooler, safer, higher maintained
The know-how’s sensible purposes lengthen far past mere commentary.
City planners may use Tree-D Fusion to in the future peer into the long run, anticipating the place rising branches may tangle with energy strains, or figuring out neighborhoods the place strategic tree placement may maximize cooling results and air high quality enhancements. They can map how bushes may reply to local weather change or cease catastrophic flooding. These predictive capabilities, the workforce says, may change city forest administration from reactive upkeep to proactive planning.

Oranger Suspendu, a dangling orange tree in Old City Jaffa by Ran Morin
“This excessive stage of specificity in tree simulation has broad purposes in forestry, the place species and genera range in development, ecological roles, and local weather resilience,” says Jan Stejskal, Assistant Professor at Czech University of Life Sciences Prague, who wasn’t concerned within the analysis. “Also, it allows metropolis planners to simulate how city forests have an effect on air high quality, shade, and biodiversity, serving to optimize tree planting for city cooling, carbon sequestration, and habitat creation, in the end fostering extra sustainable cities.”
A Tree Grows in Brooklyn (and plenty of different locations)

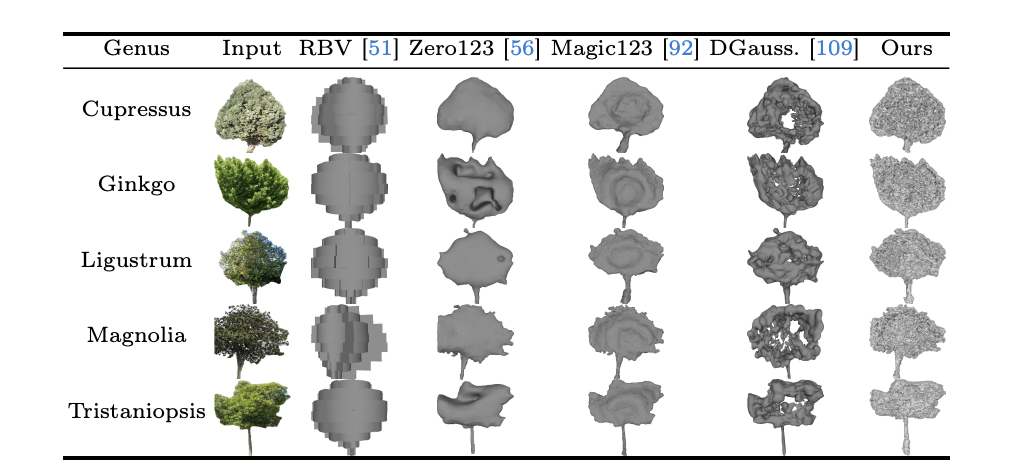
The researchers took a hybrid method to their methodology, utilizing deep studying to create a 3D envelope of every tree’s form, then utilizing conventional procedural fashions to simulate practical department and leaf patterns based mostly on the tree’s genus. This combo helped the mannequin predict how bushes would develop underneath completely different environmental circumstances and local weather situations corresponding to completely different attainable native temperatures and ranging entry to groundwater.
Now, as cities worldwide grapple with rising temperatures, the analysis gives a brand new window into the way forward for city forests. In a collaboration with MIT’s Senseable City Lab, the Purdue University and Google workforce is embarking on a world research that reimagines bushes as dwelling local weather shields. Their digital modeling system captures the intricate dance of shade patterns all through the seasons, revealing how strategic city forestry may hopefully change sweltering metropolis blocks into extra naturally cooled neighborhoods.
“Every time a road mapping automobile passes via a metropolis now, we’re not simply taking snapshots — we’re watching these city forests evolve in real-time,” says Beery. “This steady monitoring creates a dwelling digital forest that mirrors its bodily counterpart, providing cities a robust lens to watch how environmental stresses form tree well being and development patterns throughout their city panorama.”
AI-based tree modeling has emerged as an ally within the quest for environmental justice: By mapping city tree cover in unprecedented element, a sister venture from the Google AI for Nature team has helped uncover disparities in inexperienced area entry throughout completely different socioeconomic areas. “We’re not simply finding out city forests — we’re attempting to domesticate extra fairness,” says Beery. The workforce is now working carefully with ecologists and tree well being consultants to refine these fashions, making certain that as cities increase their inexperienced canopies, the advantages department out to all residents equally.
While Tree-D fusion marks some main “development” within the area, bushes may be uniquely difficult for pc imaginative and prescient methods. Unlike the inflexible constructions of buildings or automobiles that present 3D modeling methods deal with effectively, bushes are nature’s shape-shifters — swaying within the wind, interweaving branches with neighbors, and continually altering their type as they develop. The Tree-D fusion fashions are “simulation prepared” in that they’ll estimate the form of the bushes sooner or later, relying on the environmental circumstances.
“What makes this work thrilling is the way it pushes us to rethink elementary assumptions in pc imaginative and prescient,” says Beery. “While 3D scene understanding methods like photogrammetry or NERF excel at capturing static objects, bushes demand new approaches that may account for his or her dynamic nature, the place even a mild breeze can dramatically alter their construction from second to second.”
The workforce’s method of making tough structural envelopes that approximate every tree’s type has confirmed remarkably efficient, however sure points stay unsolved. Perhaps probably the most vexing is the “entangled tree drawback”, when neighboring bushes develop into one another, their intertwined branches create a puzzle that no present AI system can totally unravel.
The scientists see their dataset as a springboard for future improvements in pc imaginative and prescient, they usually’re already exploring purposes past road view imagery, trying to lengthen their method to platforms like iNaturalist and wildlife digital camera traps.
“This marks just the start for Tree-D Fusion,” says Jae Joong Lee, a Purdue University PhD pupil who developed, applied and deployed the Tree-D-Fusion algorithm. “Together with my collaborators, I envision increasing the platform’s capabilities to a planetary scale. Our objective is to make use of AI-driven insights in service of pure ecosystems – supporting biodiversity, selling international sustainability, and in the end, benefiting the well being of our complete planet.”
#wpdevar_comment_1 span,#wpdevar_comment_1 iframe{width:100% !necessary;} #wpdevar_comment_1 iframe{max-height: 100% !necessary;}
Comments
feedback








